Why Excessive Sweating? Try Effective Remedies for Hyperhidrosis
Why Excessive Sweating? Understanding Causes and Effective Management Strategies! 💦🤔 Explore insights into the factors contributing to hyperhidrosis.
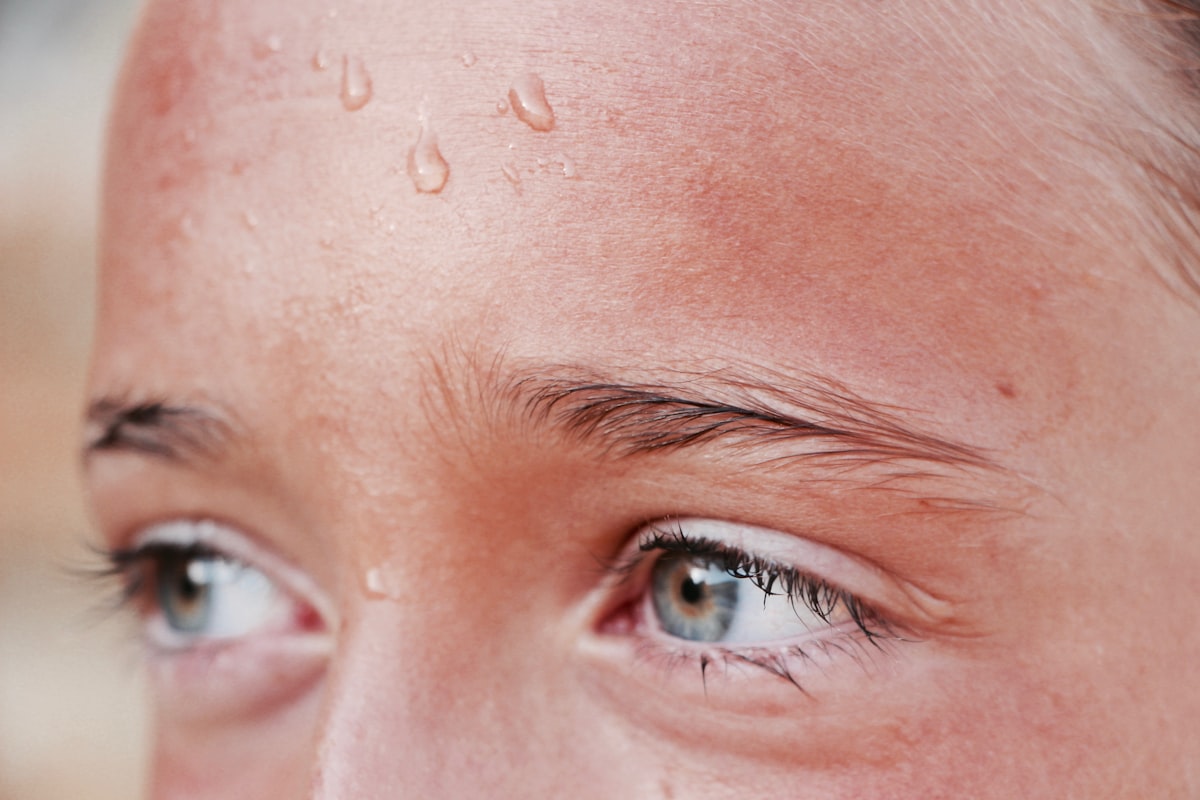
Excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It goes beyond the normal perspiration needed to regulate body temperature and can cause significant discomfort and embarrassment. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various remedies available to manage excessive sweating.
I. Introduction
Excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, is a condition characterized by sweating beyond what is necessary for the body to regulate its temperature. It affects both men and women, and its severity can vary from mild to severe. Hyperhidrosis can have a negative impact on an individual’s quality of life, leading to physical discomfort, emotional distress, and social implications.
II. Causes of Excessive Sweating
Primary Hyperhidrosis
Primary hyperhidrosis is the most common form of excessive sweating and typically begins during adolescence or early adulthood. The exact cause is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development.
- Genetic factors: Research suggests that primary hyperhidrosis may have a genetic component, as it often runs in families.
- Overactive sweat glands: Individuals with primary hyperhidrosis have overactive sweat glands, which produce more sweat than necessary.
- Triggers for excessive sweating: Certain triggers such as heat, anxiety, stress, or certain foods can exacerbate sweating in individuals with primary hyperhidrosis.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis is caused by an underlying medical condition or medication. It typically develops later in life and can affect individuals who have not previously experienced excessive sweating.
- Medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid problems, menopause, infections, and certain types of cancer can lead to secondary hyperhidrosis.
- Medications: Some medications, including antidepressants, antipyretics, and certain antibiotics, may cause excessive sweating as a side effect.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal imbalances or changes in hormone levels can trigger secondary hyperhidrosis.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to increased sweating due to the body’s need to regulate temperature.
- Anxiety and stress: Emotional factors, such as anxiety and stress, can trigger excessive sweating in some individuals.
- Neurological disorders: Certain neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease and autonomic nervous system disorders, can cause excessive sweating.
- Substance abuse: Alcohol and drug abuse can lead to excessive sweating as a side effect.
- Heat and humidity: Environmental factors, such as hot weather or high humidity levels, can naturally trigger sweating to regulate body temperature. However, individuals with hyperhidrosis may experience excessive sweating even in normal conditions.
III. Symptoms and Impact of Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating can manifest in various ways and have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life.
- Physical discomfort: Excessive sweating can lead to persistent wetness, skin irritation, and unpleasant body odor. It can also contribute to the development of fungal or bacterial infections.
- Emotional and social implications: Individuals with hyperhidrosis often experience embarrassment, low self-esteem, and social anxiety. The fear of visible sweat stains and the odor associated with excessive sweating can make social interactions challenging.
- Impact on daily life: Excessive sweating can affect a person’s professional life, personal relationships, and overall well-being. It may limit clothing choices, hinder physical activities, and cause discomfort in social settings.
IV. Diagnosis of Hyperhidrosis
If you suspect you have hyperhidrosis, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. The following steps are typically involved in diagnosing hyperhidrosis:
- Physical examination: The healthcare provider will examine the areas where sweating occurs excessively, such as the armpits, palms, soles, or face.
- Medical history assessment: Your doctor will ask about your medical history, including any medications you are taking and any other relevant symptoms.
- Additional tests: In some cases, your doctor may order certain tests, such as a sweat test, to measure the amount of sweat produced or blood tests to check for any underlying medical conditions.
Once a diagnosis of hyperhidrosis is confirmed, you and your healthcare provider can discuss appropriate treatment options.
V. Treatment Options for Excessive Sweating
The treatment approach for excessive sweating depends on the severity of the condition and the impact it has on an individual’s life. Various remedies are available to manage hyperhidrosis effectively.
Lifestyle changes
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help manage excessive sweating and reduce its impact on daily life.
- Proper hygiene practices: Shower regularly with antibacterial soap to control body odor and prevent infections. Dry the affected areas thoroughly.
- Clothing choices: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing made of natural fabrics such as cotton or linen. Avoid tight clothing that can trap sweat and increase discomfort.
- Stress management techniques: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate sweating. Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to manage stress levels effectively.
Topical treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense in managing excessive sweating.
- Antiperspirants: Over-the-counter antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can be applied to the affected areas to reduce sweating. Prescription-strength antiperspirants may be recommended for severe cases.
- Powders and creams: Talcum powders or antifungal creams can help absorb moisture, reduce friction, and prevent skin irritation.
Oral medications
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to manage excessive sweating.
- Anticholinergics: These medications help reduce sweating by blocking the chemical messenger acetylcholine, which stimulates the sweat glands. However, they may cause side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, or constipation.
- Beta-blockers: These medications primarily used to treat high blood pressure can also help reduce sweating by blocking certain nerve signals. They are generally well-tolerated but may have other potential side effects.
Botox injections
Botulinum toxin injections, commonly known as Botox, can temporarily block the nerves that stimulate sweat glands. This treatment is particularly effective for localized areas of excessive sweating, such as the armpits.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis involves passing a weak electrical current through the skin’s surface while the affected area is submerged in water. This procedure can temporarily block the sweat glands and provide relief from excessive sweating.
Surgical procedures
In severe cases where other treatments have been ineffective, surgical procedures may be considered.
- Sweat gland removal: A surgical procedure called sweat gland excision involves removing sweat glands from the affected areas. This procedure is usually reserved for severe cases of hyperhidrosis.
- Sympathectomy: Sympathectomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or clamping the nerves responsible for stimulating the sweat glands. It is primarily used for severe cases of hyperhidrosis affecting the palms or face.
VI. Natural Remedies for Excessive Sweating
In addition to medical treatments, several natural remedies can help manage excessive sweating.
Herbal remedies
- Sage tea: Sage has natural astringent properties and can help reduce excessive sweating. Drinking sage tea or applying sage-infused products to the affected areas may provide relief.
- Witch hazel: Witch hazel acts as a natural astringent and can help tighten the skin’s pores, reducing sweat production.
- Apple cider vinegar: Applying diluted apple cider vinegar to the affected areas can help balance the skin’s pH levels and reduce excessive sweating.
Dietary changes
Certain dietary modifications can help manage hyperhidrosis.
- Avoidance of trigger foods: Spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can trigger sweating in some individuals. Limiting or avoiding these foods and beverages may help reduce excessive sweating.
- Increased water intake: Staying hydrated can help regulate body temperature and reduce sweating. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- B-vitamin supplementation: Some studies suggest that B vitamins, particularly vitamin B-12, may help regulate sweat production. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Stress reduction techniques
Stress and anxiety can worsen excessive sweating. Engaging in stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and reduce sweating episodes.
VII. Managing Hyperhidrosis in Specific Areas of the Body
Excessive sweating can occur in specific areas of the body, requiring targeted management approaches.
- Excessive facial sweating: Facial sweating can be managed by using facial antiperspirants, applying absorbent facial powders, or considering Botox injections in specific facial areas.
- Excessive underarm sweating: Underarm sweating can be controlled by using clinical-strength antiperspirants, wearing moisture-wicking fabrics, or opting for underarm sweat pads.

- Excessive palm and sole sweating: Iontophoresis, oral medications, or Botox injections can be effective in managing excessive sweating of the palms and soles.
Excessive sweating can also occur in the inner parts of the body, causing discomfort and inconvenience. Here are some remedies to manage excessive sweating in these areas:
-
Excessive chest and back sweating:
Excessive sweating in the chest and back region can be bothersome, especially during physical activities or warm weather. To manage excessive sweating in these areas, consider the following remedies:
- Breathable clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics like cotton or linen. These fabrics allow air circulation and can help minimize sweat accumulation.
- Absorbent pads: Place absorbent pads or sweat shields under your clothing to absorb excess moisture and protect against sweat stains.
- Antiperspirant powders: Use antiperspirant powders specifically formulated for larger body areas. These powders help absorb moisture and reduce sweating.
Excessive groin sweating:
Excessive sweating in the groin area can cause discomfort, chafing, and unpleasant odors. To manage excessive groin sweating, consider the following remedies:
- Moisture-wicking underwear: Choose moisture-wicking underwear made of materials like moisture-wicking polyester or bamboo fibers. These fabrics draw moisture away from the skin, keeping the area drier.
- Loose-fitting clothing: Opt for loose-fitting pants or shorts to allow air circulation and minimize sweat accumulation in the groin area.
- Talcum powder: Apply talcum powder or cornstarch to the groin area to help absorb moisture and reduce friction.
Excessive sweating in intimate areas:
Excessive sweating in intimate areas can be uncomfortable and may lead to irritation or infections. To manage excessive sweating in these areas, consider the following remedies:
- Hygiene practices: Maintain good hygiene by washing the area with mild, fragrance-free soap and warm water. Pat the area dry thoroughly.
- Cotton underwear: Wear underwear made of breathable cotton fabric to allow proper airflow and reduce moisture buildup.
- Antifungal powders or creams: Use antifungal powders or creams recommended by a healthcare professional to prevent fungal infections in intimate areas.
Remember, if you experience excessive sweating in inner body parts that significantly affects your daily life, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist. They can provide personalized advice and recommend suitable treatment options.
VIII. Coping with Hyperhidrosis
Living with hyperhidrosis can be challenging, but several strategies can help individuals cope with the condition effectively.
- Support groups: Joining support groups or online communities can provide a sense of understanding, validation, and support from others experiencing similar challenges.
- Seeking professional help: Consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist who specializes in hyperhidrosis. They can offer personalized advice, treatment options, and ongoing support.
- Emotional well-being strategies: Practice self-care, engage in activities that boost your self-esteem and confidence, and develop coping mechanisms to manage stress and anxiety associated with hyperhidrosis.
IX. Conclusion
Excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. However, there are various remedies and treatment options available to manage this condition effectively. From lifestyle changes and topical treatments to oral medications and surgical procedures, individuals can find relief and regain control over their excessive sweating. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
X. FAQs
Here are a few commonly asked questions about excessive sweating:
1. Can excessive sweating be cured?
While there is no permanent cure for hyperhidrosis, various treatment options can help manage and reduce excessive sweating effectively.
2. Are there any home remedies that can help with hyperhidrosis?
Yes, several home remedies such as sage tea, witch hazel, and apple cider vinegar can provide relief from excessive sweating. However, their effectiveness may vary among individuals.
3. Are there any lifestyle changes that can reduce excessive sweating?
Yes, adopting certain lifestyle changes such as proper hygiene practices, clothing choices, and stress management techniques can help reduce excessive sweating.
4. Can excessive sweating be a sign of an underlying medical condition?
Yes, excessive sweating can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. If you experience excessive sweating, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
5. Can hyperhidrosis be inherited?
Yes, primary hyperhidrosis can run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.



