How to Treat Recurring Boils- A Complete Guide
How to Treat Recurring Boils: Effective Solutions for Long-Term Relief! 🩹🌡️ Discover practical tips to manage and prevent the recurrence of painful boils.
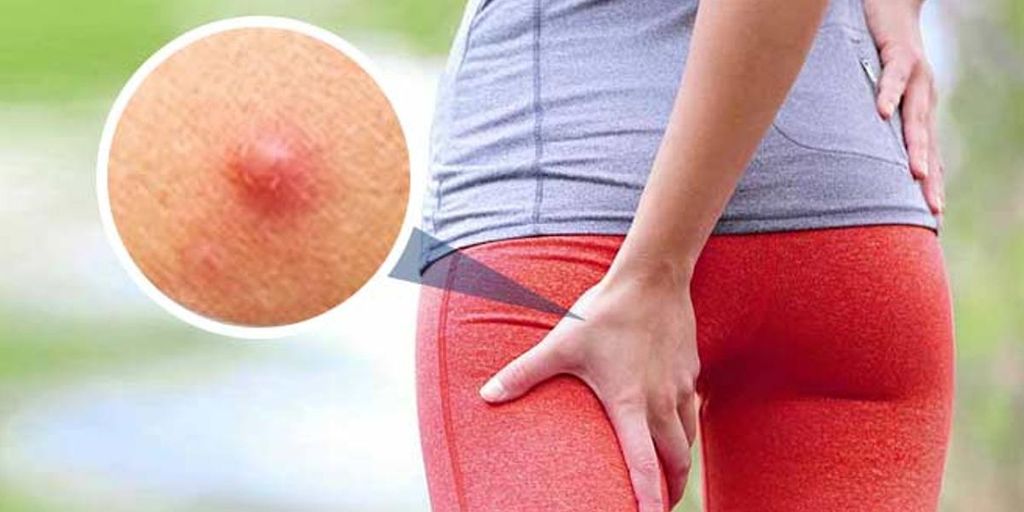

Recurring boils on the buttocks, inner thighs, and other body parts can be a bothersome and uncomfortable condition. Boils are painful, pus-filled bumps that develop on the skin’s surface, often caused by an infection of hair follicles. While boils can occur anywhere on the body, they are particularly common on the buttocks due to the high concentration of sweat glands in that area. Here, we will explore the causes of recurring boils on various body parts and discuss effective treatment options.
Understanding Recurring Boils
What are boils?
Boils, also known as furuncles, are localized infections that begin as red, tender bumps on the skin. As the infection progresses, they become larger and filled with pus. Boils are usually caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which enters the skin through cuts or breaks, infecting hair follicles and surrounding tissues. Blister, abscess, carbuncle, sore, and pimple are other synonyms for boil.
Where Do They Occur?
Recurring boils can appear on various parts of the body, but certain areas are more prone to their development. Here are some common locations where recurring boils occur:
- Face and neck: Boils can occur on the face, particularly around the nose, cheeks, and chin. The presence of hair follicles and oil glands in these areas increases the risk of bacterial infection and subsequent boil formation.
- Armpits: The warm and moist environment of the armpits provide an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. Friction from clothing and the presence of sweat glands can contribute to the occurrence of recurring boils in this area.
- Groin: The folds and creases in the groin area are susceptible to friction and sweat buildup, making it a common site for recurring boils. This can be particularly uncomfortable and bothersome due to constant movement and irritation.
- Buttocks: The buttocks are prone to friction, especially during activities like sitting or exercising. Prolonged pressure and sweat accumulation in this area can contribute to the development of recurring boils.
- Inner thighs: Friction and sweat between the inner thighs can create an environment conducive to the formation of boils. The proximity of the inner thighs and the frequent rubbing make this area prone to recurring boils.
- Under the breasts: The skin underneath the breasts can experience friction and moisture, especially in warm and humid conditions. This can lead to bacterial growth and the recurrence of boils.
- Back of the neck: The back of the neck is another area where recurring boils may occur, particularly in individuals with long hair. The combination of hair follicles, sweat, and oil glands increases the likelihood of boil formation.
It’s important to note that boils can develop on any part of the body where there are hair follicles and the presence of bacteria. Understanding the common locations can help individuals take preventive measures, maintain good hygiene, and seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
Causes of recurring boils
Recurring boils on the buttocks can have various underlying causes. These include poor hygiene, friction from tight clothing, weakened immune system, diabetes, and obesity. Additionally, individuals with a history of boils or those who come into close contact with others who have blisters may be more prone to recurring boils. While boils can occur on any part of the body, they are common on the buttocks and inner thighs due to friction and sweat buildup in that area.
Recurring boils can be frustrating and uncomfortable. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial in managing and preventing their recurrence. Here are some common factors that contribute to the development of recurring boils:
- Bacterial infection: The primary cause of boils is a bacterial infection, usually from Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. These bacteria can enter the body through cuts, breaks in the skin, or hair follicles, leading to an infection that results in boils. Recurrence can occur when the bacteria persist on the skin or in the body.
- Weakened immune system: A weakened immune system makes it harder for the body to fight off infections, including bacterial infections that cause boils. Factors that can weaken the immune system include chronic illnesses, certain medications, poor nutrition, stress, and lack of sleep.
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate hygiene practices can contribute to recurring boils. Failure to maintain cleanliness, especially in areas prone to sweat and friction, can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Regular washing and proper hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing boils.
- Close contact with carriers: Coming into close contact with individuals who are carriers of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria can increase the risk of developing recurring boils. Sharing personal items, such as towels, clothing, or razors, can facilitate the transfer of bacteria.
- Chronic skin conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as acne, eczema, or folliculitis, can make the skin more susceptible to bacterial infections and the formation of boils. Recurrent boils may occur in areas affected by these conditions.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to developing recurring boils due to high blood sugar levels, which can impair the immune system’s ability to fight infections effectively.
- Friction and sweat: Areas of the body where there is friction, such as the inner thighs or buttocks, are more susceptible to recurring boils. Friction and sweat can cause irritation and create an environment where bacteria thrive.
- Nasal carriage: Some individuals naturally carry Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in their nasal passages without experiencing any symptoms. However, these carriers can unknowingly spread the bacteria to other parts of their body, leading to recurrent boils.
Understanding the causes of recurring boils can help individuals take appropriate preventive measures and seek effective treatments. Maintaining good hygiene, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and addressing underlying health conditions are key to managing and reducing the recurrence of boils.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
To prevent the recurrence of boils on the buttocks, inner thighs, and other body parts significant lifestyle changes and hygiene practices can be beneficial.
- Proper hygiene practices
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing recurring boils. Regularly wash the affected area with a gentle cleanser and warm water. Avoid harsh soaps or scrubbing vigorously, as it can irritate the skin and worsen the condition.
- Wear loose and breathable clothing
Tight clothing can increase friction and moisture, creating an environment favorable for bacterial growth. Opt for loose, breathable clothing made from natural fibers like cotton to reduce friction and promote airflow.
- Avoid tight-fitting underwear
Tight-fitting underwear can trap sweat and moisture, leading to bacterial growth and the formation of boils. Choose underwear made from moisture-wicking materials and ensure it fits comfortably without excessive tightness.
- Maintain a healthy diet
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in supporting a healthy immune system. Incorporate foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water.
- Maintain a healthy immune system
A strong immune system plays a crucial role in preventing and managing infections. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by doing regular exercise, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep. These practices can help boost your immune system and reduce the frequency of recurring boils.
Recurring Boils: Treatment Options
When dealing with recurring boils on the buttocks, thighs, and other body parts, various treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further infection.
- Warm compresses
Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help promote blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and facilitate the natural draining of the boil. Soak a clean washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and place it over the blister for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
- Antibiotic ointments
Over-the-counter antibiotic ointments, such as neomycin or bacitracin, can be applied topically to the boil to help fight off the infection and promote healing. Follow the instructions provided on the product packaging.
- Topical antiseptics
Antiseptic solutions like povidone-iodine or hydrogen peroxide can be used to clean the affected area and prevent the spread of infection. Apply the antiseptic solution with a cotton ball or swab, gently dabbing the boil and the surrounding skin.
- Oral antibiotics
For severe or recurrent cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed by a healthcare professional. These antibiotics help eradicate the infection from within the body, reducing the likelihood of future boils.
- Incision and drainage
In certain situations, a healthcare professional may need to perform a minor surgical procedure to drain the pus from the boil. This helps alleviate pain and promotes faster healing.
- Medical procedures
In rare cases of chronic or severe recurring boils, medical procedures like laser hair removal, carbuncle removal, or sweat gland removal may be recommended to prevent future occurrences.
Home Remedies for recurring boils
In addition to medical treatments, several natural remedies can help complement the healing process and provide relief from recurring boils on the buttocks.
- Tea tree oil
Tea tree oil possesses antimicrobial properties that can combat the bacteria responsible for boils. Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil with carrier oil like coconut oil, and apply it to the affected area using a cotton ball.
- Turmeric paste
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Create a paste by mixing turmeric powder with water and applying it to the boil. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off.
- Aloe vera gel
Aloe vera gel has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with boils. Apply a thin layer of fresh aloe vera gel to the affected area and leave it on until it dries.
- Epsom salt bath
Taking a warm bath with Epsom salt can provide relief from the discomfort of boils. Dissolve Epsom salt in warm water and soak in it for 15-20 minutes. Gently pat the skin dry after the bath.
Remember that while natural remedies can be helpful, they may not work for everyone or in severe cases. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking medications.
When it comes to treating recurring boils on the buttocks, a combination of proper hygiene, medical interventions, and natural remedies can significantly improve the condition and prevent future recurrences.
When to Seek Medical Help
While most cases of recurring boils on the buttocks can be managed at home, certain situations require medical attention. Consult a healthcare professional if:
- The boil is extremely painful or keeps getting larger.
- The abscess is accompanied by fever or other signs of infection.
- The boils are recurring frequently or not healing.
- The surrounding skin becomes red, warm, or swollen.
- There are signs of spreading infection, such as red streaks.
Conclusion
Recurring boils on the buttocks can be a persistent and uncomfortable condition. By adopting preventive measures, practicing good hygiene, and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage and reduce the recurrence of boils. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for severe or persistent cases to receive proper diagnosis and guidance.
FAQs
Here are some commonly asked questions about recurring boils and their answers:
- Are recurring boils contagious?
Recurring boils are generally not contagious. However, the bacteria-causing boils can spread through direct contact with the pus or drainage from the boils. It is essential to maintain good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items to minimize the risk of transmission.
- Can stress contribute to recurring boils?
Stress can potentially weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. While stress alone may not directly cause boils, it can contribute to a compromised immune response, increasing the likelihood of recurring boils.
- Are there any complications of recurring boils?
If left untreated or not properly managed, recurring boils can lead to complications such as cellulitis (skin infection), abscess formation, scarring, or the development of a chronic condition known as hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Can diet affect the occurrence of boils?
A healthy diet can support a robust immune system, which is crucial in preventing infections, including boils. However, there is limited scientific evidence linking specific foods to the occurrence of boils. It is generally recommended to maintain a balanced diet for overall well-being.
- Can recurring boils be a sign of an underlying health condition?
In some cases, recurring boils can be a symptom of an underlying health condition, such as diabetes, a weakened immune system, or an autoimmune disorder. If you experience persistent boils, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
- When should I seek medical help for recurring boils?
If you experience severe pain, the boil worsens, or you have recurrent or persistent boils, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- What should I do if a boil doesn’t heal or keeps coming back?
If a boil doesn’t heal within a week or keeps recurring, it’s recommended to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment, and determine if further evaluation or testing is necessary.



