Occipital Neuralgia: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management
Occipital Neuralgia: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for This Painful Condition. 🧠💊
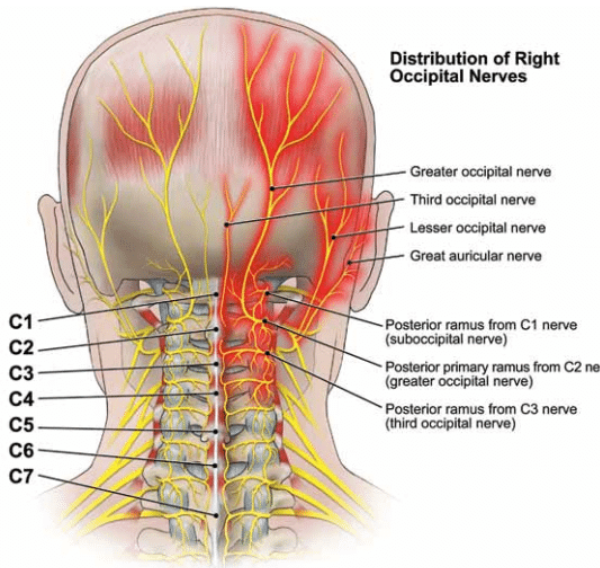
Occipital neuralgia is a condition characterized by severe, stabbing pain in the back of the head and neck, often radiating to the scalp. This excruciating pain can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the details of occipital neuralgia, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and effective management strategies.
What is Occipital Neuralgia?
Occipital neuralgia is a neurological condition that affects the occipital nerves, which run from the base of the skull to the top of the neck. These nerves can become irritated or inflamed, leading to severe pain that resembles an electric shock or shooting sensation. The pain typically occurs on one side of the head and may radiate to the scalp, forehead, and behind the eyes.
Occipital Neuralgia Pain Areas
The pain associated with occipital neuralgia can manifest in specific areas of the head and neck:
- Back of the Head: The most common area affected by pain is the back of the head, often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation.
- Scalp: Pain may radiate to the scalp, creating a sensation of intense pressure or burning.
- Forehead: Some individuals may experience pain that extends to the forehead, resembling a tension headache.
- Behind the Eyes: The pain can also spread behind the eyes, leading to discomfort and sensitivity to light.
The exact distribution of pain can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience pain in multiple areas simultaneously.
Occipital Neuralgia Common Symptoms
Individuals experiencing occipital neuralgia often report a range of distressing symptoms, which may include:
- Severe Head Pain: A sharp, stabbing pain concentrated in the back of the head.
- Radiating Discomfort: The pain may extend from the base of the skull to the scalp, often affecting one side.
- Scalp Sensitivity: The scalp can become tender to the touch, and even mild pressure may trigger pain.
- Visual Disturbances: Some individuals may experience sensitivity to light (photophobia) and disturbances in vision.
- Neck Pain: Pain may radiate down the neck and even extend to the upper back.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be episodic or persistent. It’s essential to seek medical evaluation if you experience any of these symptoms to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Potential Causes
The exact causes of occipital neuralgia can vary, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Compression or Irritation: Compression of the occipital nerves due to tense muscles or tightness in the neck can lead to neuralgia.
- Trauma: Previous head or neck injuries, such as whiplash, may damage the occipital nerves.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like osteoarthritis, cervical disc disease, and infections can irritate the nerves.
- Inflammation: Inflammation of the blood vessels near the nerves can cause irritation.
- Anatomical Variations: Sometimes, the occipital nerves may pass through muscles or other structures, leading to friction and irritation.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Proper diagnosis is essential to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms. A healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical evaluation, which may include:
- Physical Examination: Assessing tenderness, sensitivity, and neck mobility.
- Medical History: Gathering information about past injuries, medical conditions, and family history.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to visualize the head, neck, and nerves.
Effective Treatment Approaches
Managing occipital neuralgia involves a comprehensive approach tailored to each individual’s needs:
Medications for Pain Relief
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescription medications can provide relief.
- Muscle Relaxants: These can help reduce muscle tension and alleviate nerve irritation.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Neck Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve neck posture and reduce strain.
- Posture Correction: Learning proper posture techniques can prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
Nerve Block Injections
- Occipital Nerve Blocks: Local anesthetics and steroids injected around the occipital nerves can provide significant pain relief.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques and stress reduction can prevent muscle tension.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring proper ergonomics at work and home can reduce strain on the neck.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
- Acupuncture: Thin needles inserted at specific points may alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
- Biofeedback: Learning to control physiological responses can help manage pain.
Coping Strategies for Occipital Neuralgia
Coping with occipital neuralgia requires a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects. Some strategies include:
- Pain Management Techniques: Utilizing pain-relief strategies such as medications, physical therapy, and relaxation techniques.
- Stress Reduction: Practicing stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness.
- Supportive Network: Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making changes to daily routines and activities to minimize pain triggers.
- Emotional Well-being: Engaging in activities that promote emotional well-being, such as hobbies, art, and spending time with loved ones.
Occipital Neuralgia Home Remedies
While medical treatment is essential, there are several home remedies that may provide relief from occipital neuralgia:
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying a warm or cold compress to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Gentle Neck Stretches: Engaging in gentle neck stretches and range-of-motion exercises can alleviate tension and promote relaxation.
- Massage: Massaging the neck and scalp can help relax tense muscles and improve blood flow.
- Aromatherapy: Using essential oils like lavender or peppermint in a diffuser can have a calming effect and potentially reduce pain.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support overall well-being.
- Yoga and Meditation: Practicing yoga and meditation can reduce stress, improve posture, and contribute to pain management.
Occipital Neuralgia Exercises
Engaging in specific exercises can help alleviate tension, improve neck posture, and reduce the frequency of occipital neuralgia flare-ups. Here are some exercises that may be beneficial:
- Neck Stretches: Gently tilt your head to the side, bringing your ear toward your shoulder. Hold for 15-30 seconds on each side.
- Chin Tucks: While sitting or standing, gently tuck your chin in towards your chest, creating a double chin. Hold for a few seconds and repeat.
- Neck Rotation: Slowly turn your head to one side, looking over your shoulder. Hold for a few seconds and repeat on the other side.
- Shoulder Shrugs: Lift your shoulders towards your ears, hold for a few seconds, and then relax.
- Head Tilts: Tilt your head to the front, back, and side, holding each position for a few seconds.
- Resistance Exercises: Place your hand on your forehead and gently press your head against your hand, holding for a few seconds. Repeat with your hand on the back of your head.
It’s essential to perform these exercises gently and without causing additional pain. Consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise routine, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms consistent with occipital neuralgia, especially if:
- Pain Severity: The pain is severe and persistent, affecting your ability to carry out daily activities.
- Progressive Symptoms: The pain worsens over time or is accompanied by new neurological symptoms, such as weakness or numbness.
- Head Trauma: You have experienced a head or neck injury, and the pain develops afterward.
- Unexplained Symptoms: You have unexplained symptoms such as visual disturbances, difficulty speaking, or changes in consciousness.
- Unresponsive to Home Remedies: Over-the-counter pain medications or home remedies provide minimal relief.
- Impact on Daily Life: The pain significantly affects your sleep, work, or social interactions.
- Recurrent Headaches: You experience recurrent, severe headaches that are not relieved by typical headache treatments.
- Underlying Conditions: You have underlying medical conditions that may contribute to or exacerbate the pain.
Seeking prompt medical attention can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and ensure appropriate treatment and management.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of occipital neuralgia on daily life can be profound and challenging. The constant, intense pain can hinder a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks and participate in activities they once enjoyed. The following are ways in which occipital neuralgia can affect daily life:
- Disrupted Sleep: The pain can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to sleep deprivation and fatigue.
- Impaired Concentration: The constant pain and discomfort can make it challenging to focus on work, studies, or other tasks.
- Reduced Productivity: Individuals with occipital neuralgia may find it challenging to complete tasks efficiently due to the distraction of pain.
- Limitations in Physical Activities: Activities that involve neck movements or physical exertion may trigger or worsen the pain, leading to limitations in exercise and other activities.
- Emotional Impact: Living with chronic pain can lead to emotional distress, including anxiety, depression, and frustration.
- Social Isolation: The pain and its impact on daily life may lead to decreased social interactions and a sense of isolation.
- Effect on Relationships: The condition can strain relationships with family, friends, and partners due to the challenges it poses.
Promising Research and Future Directions
As medical research continues to advance, there is a growing interest in understanding occipital neuralgia more comprehensively. Promising research and future directions in the field include:
- Neuromodulation Techniques: Researchers are exploring innovative neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), to target and alleviate occipital neuralgia symptoms.
- Genetic Studies: Genetic research aims to identify potential genetic factors that may contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to occipital neuralgia, leading to personalized treatment approaches.
- Biologics and Nerve Growth Factors: Some studies focus on the use of biologic agents and nerve growth factors to promote nerve healing and reduce inflammation associated with occipital neuralgia.
- Advancements in Imaging: High-resolution imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), are being employed to visualize neural activity and understand the neural pathways involved in occipital neuralgia.
- Targeted Therapies: Researchers are exploring targeted therapies that aim to interrupt pain signals specifically related to occipital neuralgia, offering more precise and effective pain relief.
- Multidisciplinary Approaches: Integrative approaches that combine medical, physical, and psychological therapies are being studied to provide comprehensive care for individuals with occipital neuralgia.
While these research areas hold promise, it’s important to note that further studies and clinical trials are needed to fully validate their effectiveness and safety in treating occipital neuralgia.
Conclusion
Living with occipital neuralgia can be challenging, but it is essential to remember that you are not alone. With the right knowledge, support, and management strategies, individuals can effectively cope with this condition and improve their overall well-being.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of occipital neuralgia, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. While there may not be a permanent cure, various approaches, including medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies, can help manage symptoms and enhance quality of life.
By staying informed about the latest research and advancements in occipital neuralgia, individuals and healthcare professionals can work together to develop tailored treatment plans that address specific needs and provide relief.
Remember, your journey towards better health starts with understanding and proactive management. With the right tools and support, you can navigate the challenges of occipital neuralgia and strive for a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
FAQs
- Q1: Can occipital neuralgia be cured completely?
- Currently, there is no permanent cure for occipital neuralgia. However, effective management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Q2: What are the common triggers for occipital neuralgia pain?
- Common triggers may include neck movements, poor posture, stress, tension, and activities that strain the neck muscles.
- Q3: Are there any specific medications for treating occipital neuralgia?
- Depending on the individual, medications such as pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and nerve-stabilizing drugs may be prescribed.
- Q4: What is the significance of lifestyle modifications in managing occipital neuralgia?
- Lifestyle modifications, including maintaining good posture, managing stress, and avoiding triggers, can help prevent or minimize occipital neuralgia flare-ups.
- Q5; How can physical therapy help with occipital neuralgia?
- Physical therapy involves exercises and techniques to improve neck strength, flexibility, and posture, which can reduce pain and prevent recurrences.
- Q6: Can occipital neuralgia affect both sides of the head?
- While occipital neuralgia often affects one side of the head, it is possible for some individuals to experience symptoms on both sides.
- Q7: Is occipital neuralgia a rare condition?
- Occipital neuralgia is relatively uncommon, but it can cause significant discomfort for those affected.
- Q8: Can stress and anxiety worsen occipital neuralgia symptoms?
- Yes, stress and anxiety can contribute to muscle tension and exacerbate occipital neuralgia symptoms.
- Q9: Are there alternative therapies that may provide relief for occipital neuralgia?
- Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and biofeedback.
- Q10: Is occipital neuralgia associated with any other medical conditions?
- Occipital neuralgia can sometimes occur as a symptom of other underlying conditions such as cervical spine issues or inflammation.



